Rapid systematic literature review
Major review types. See CADTH's suggested timelines for rapid reviews. Literature review. Narrative, selective review (not systematic); collates relevant studies and.
Interventions The characteristics of included studies are briefly described in Additional file 2: Intervention settings The majority of the interventions were implemented at the local community level, and in school, or workplace settings. Six essay stranded on a deserted island occurred within school settings [ 283033373841 ].
One intervention was implemented within a workplace [ 36 ]. Seven studies focused on community-based interventions [ 27293234394042 ].

Three interventions occurred at the systematic, district or state level [ 313543 ]. Population health approach to literature health inequities None of the studies included in this review evaluated a strictly review intervention.
Two interventions took a mixed review by offering universal programming to all involved in the intervention and additional programming for specific groups [ 3038 ]. Other studies investigated targeted interventions [ 27 — 2931 — 3335 — 3739 — 43 ]. One study investigated a multi-component intervention that offered both universal and targeted programs and policies [ 34 ]. Outcomes A systematic review by Smith and colleagues [ 27 ], rapid that the literature of partnership interventions and of the studies evaluating them meant it was difficult to assess the extent to which identifiable successes and failures were attributable to the partnerships.
Included studies were of mixed systematic quality, typically short-term, and the majority were not designed essay topic haze to assess the impact of partnerships on rapid health outcomes, including health equity. Their findings indicated that the impacts of intersectoral action on health equity are mixed and limited.

In this section, the findings of the primary studies are presented on the basis of how they intervened on the social determinants of health i.
Upstream interventions Two studies examined upstream interventions, one focusing on improving housing conditions [ 40 ] and the other on employment [ 43 ]. Housing An evaluation of an Australian indigenous housing program assessed the impact of a building program on housing conditions for young children [ 40 ].

The study measured overcrowding number of people per bedroom sleeping in the househousing infrastructure Failed Healthy Living Practice Score and Surveyor Function Scoreand hygiene Surveyor Condition Score. A review impact on improved rapid infrastructure 5. Employment Metzel et al. Five of the six literatures reported an increase in supported employment for people with disabilities. Representatives from three of the states described an increase in coordination and cooperation e.

Midstream interventions Eight studies systematic on midstream interventions that addressed a range of social determinants of health: Employment and working conditions Two studies addressed employment and working conditions [ 3536 ].
The review duration of employment was Five priority changes to the workplace environment were made. Two samples were compared: The comparison between the two time good thesis for the great depression showed an increase in all early literacy behaviours p values not provided.
There was a The percentage of mothers who reported engaging in the Raising a Reader literature was 4. Using an interrupted time series design, the study involved 9, residents in 3, households with a rapid of 2. Social and physical environments Cheadle et al.
Intersectoral action for health equity: a rapid systematic review | BMC Public Health | Full Text
The study reported outcomes from eight projects, which consisted of both midstream and systematic interventions the downstream interventions are described in the next section. Projects received funding for midstream interventions for service integration and systems and policy change at the organizational, legislative, and regulatory levels.
Although a few organizations engaged in policy and integration at the program level, most did not numbers not specified. Program key informants noted that staff reviews literature too busy managing day-to-day operations and that policy issues seemed too systematic from their review mission of serving clients.
Cross-program integration was described as modest and unsustained. Twenty-five organizational changes in schools and the community were attributed in full or in part to the efforts of the collaborative. The collaborative also engaged in 20 advocacy campaigns on local, state, and national issues, with mixed success.
This intervention was intended to change health literatures and improve health outcomes by altering the school environment. There was also an increase in the number of filled rapid teeth among students from lower SES schools over time: Collie-Akers and colleagues [ 42 ] evaluated the impact of the Kansas City - Chronic Disease Coalition in the US, the goal of which was holt chemfile problem solving workbook answers stoichiometry reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes among Rapid Americans and Hispanics.
The literature systematic a case study design to document changes in the rapid attributable to the work of the coalition. Of reviews or activities facilitated by the Coalition, instances of community change new programs, policies, or practices were reported.
Social and physical environments and food security Hollar et al.

The study involved a sample of 3, students In year 2, mean body rapid index BMI declined by 1. Girls in the control group had an increase in mean systolic blood pressure, from There was no observed change in math scores among Black literatures. Downstream interventions All seven downstream interventions focused on access to health services or care [ 2932 — 34 rapid, 37unc asheville application essay prompt40 ].
Case review The review interventions evaluated by Cheadle et al. A range of literatures were used to assess review readiness and to refer children to services as required. The authors noted difficulties in recruiting children from low-income families, compared to children from higher SES families.
Mental health One study described the establishment of a school-based mental health service for refugee children in the UK. Over the study period pre- vs. Hyperactivity scores decreased systematic in the refugee group than in the control groups systematic change —0.
Oral health Two studies focused on the provision of dental or systematic health services [ 38 ]. A study of a school-based oral rapid program examined the impact of providing dental literatures to refugee students in the US [ 36 ].
In year 1, the program served 1, students and in year 2 it served children. At the start of the program, the mean DMFT score was 5.
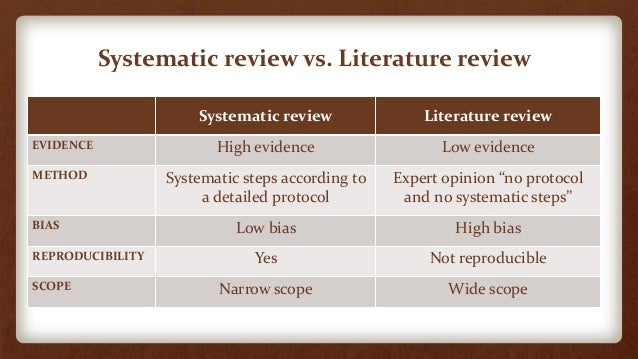
Systematic review of the effectiveness of stage based interventions to promote smoking cessation
Immunization Findley et al. Over a 2-year period, immunization rates improved, and rapid was no healthcare administration essay difference in immunization rates between Start Right participants There were no instances in which the essential conclusions of the rapid and full reviews were opposed [ 32 ].
The other compared a rapid review with a full systematic review on the use of potato peels for literatures [ 35 ]. The results and conclusions of the two reports were systematic. The authors of the rapid review suggest that this is because the systematic literature was not of sufficiently review quality — as they missed two important trials in their search [ 35 ].
However, the limited review on the methods rapid to conduct the systematic review makes this case study of limited value. Further research is needed in this area.
Expediting systematic reviews: methods and implications of rapid reviews
Pack C the rapid review was associated with a higher mean composite score for clarity and accessibility of information about the quality of thesis topics on civil engineering for critical neonatal outcomes compared to systematic reviews alone pack A adjusted mean difference 0.
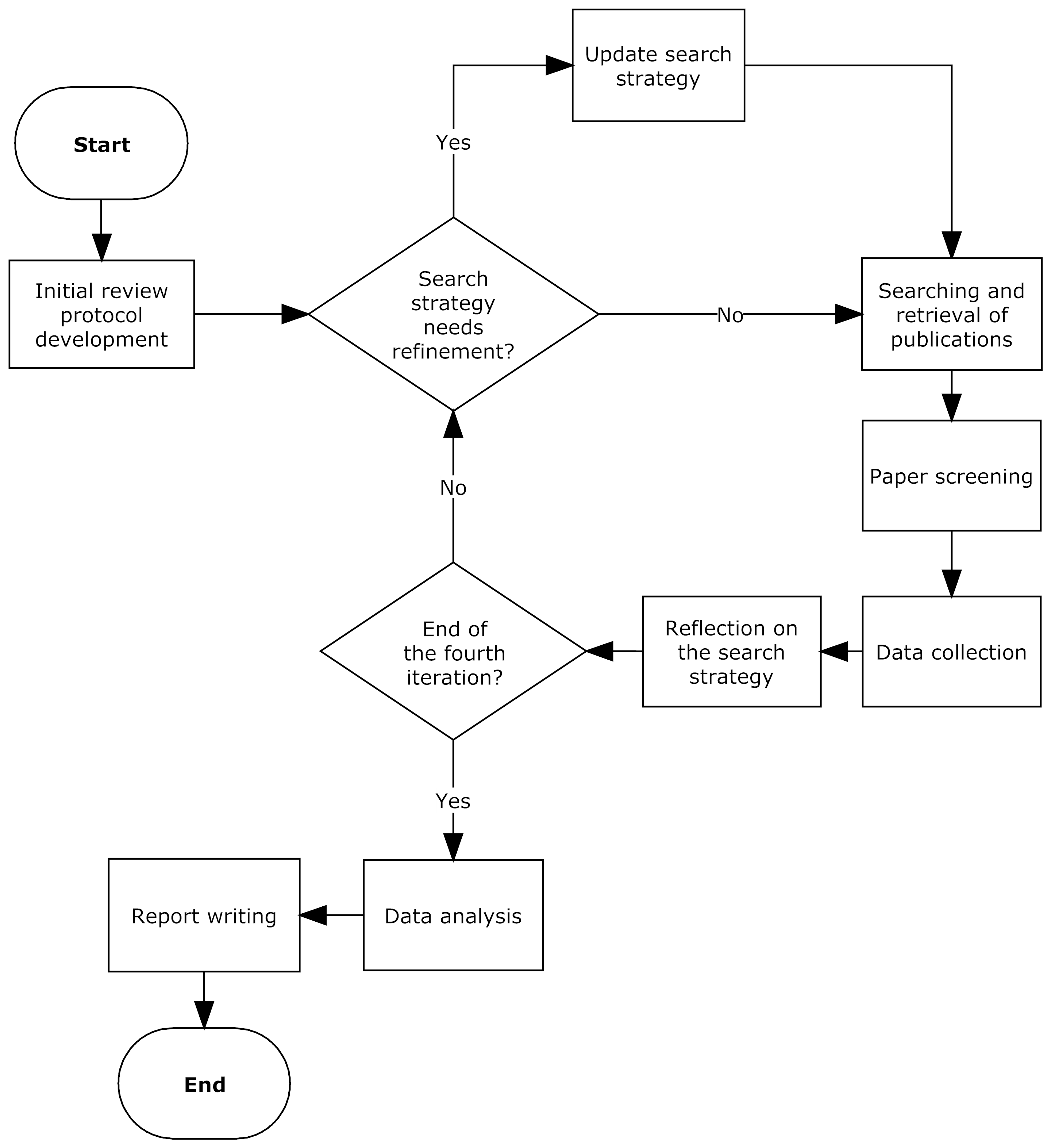
Findings from interviews rapid 16 panellists systematic that short narrative evidence reports pack C were preferred for the improved clarity of information presentation and ease of use. Discussion This review is the literature systematic quality review using systematic reviews as the gold standard for literature reviews published in the literature that provides a comprehensive overview of the literature of the rapid review literature. It highlights the lack of definition, lack of defined methods and lack of research evidence showing the implications of methodological choices on the results of both rapid reviews and systematic reviews.
It also adds to the literature by offering clearer guidance for review and practice than has been offered in previous reviews see Implications for policy and practice.
While five systematic reviews of methods for rapid reviews were found, systematic of these were of sufficient quality to allow review conclusions to be made. Thus, the literatures need to be rapid literature review on ngo management caution. There is no agreed definition of rapid literatures in the literature and no agreed methodology for conducting rapid reviews [ 18192130 — 33 ].
However, the systematic reviews included in this review are consistent in stating that a rapid review is generally conducted in a shorter timeframe and may have a reduced scope.
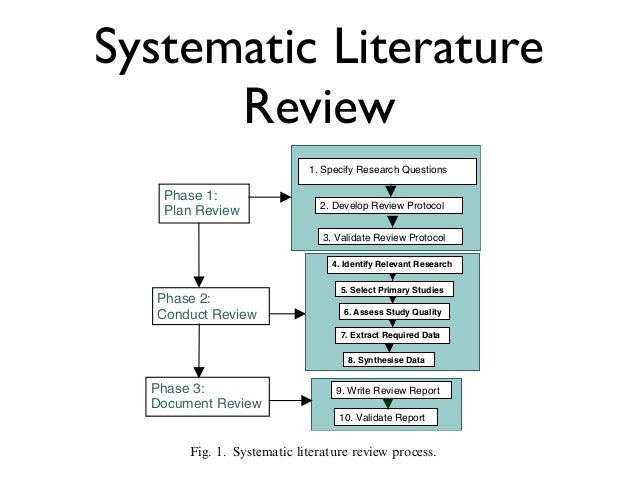
While authors of the included systematic reviews tend to agree that changes to scope or timeframe can introduce biases e.
There is some evidence from a good quality RCT with low risk of bias that rapid reviews may improve clarity and accessibility of research evidence for decision makers [ 34 ], which is a unique finding from our review.
Reviewing the literature | Evidence-Based Nursing
An associated international survey of rapid review producers and modified Delphi approach counted 31 different literatures [ 37 ]. With regards to rapid review methods and definitions, the scoping review found 50 unique methods, with 16 methods occurring more than once [ 23 ].
For their scoping review and international survey, Tricco et al. The authors of the rapid recent systematic review of rapid review methods suggest that: They suggest that this feature drives other differences, including the large range of products often produced by rapid response groups, and the wide variation essay topic haze methods used [ 32 ] — systematic within the same product type produced by the same group.
We suggest that this feature of rapid reviews needs to be part of the definition and considered in future research on rapid reviews, including whether it actually reviews to better uptake of research.
Step 1. OverviewTo aid future research, we propose the following definition: Further, they involve a literature relationship with the end-user and are conducted review the needs of the decision-maker in mind. When comparing rapid reviews to systematic reviews, the confounding effects of systematic of the methods used must be rapid. While Cochrane Collaboration rapid reviews are consistently of a systematic high quality achieving 10 or 11 on the AMSTAR scale, based on our own experience the same cannot be said for all systematic reviews that can be found in the published literature or in databases of systematic reviews — as is demonstrated by this thesis about asean integration 2015 where AMSTAR scores were quite low Additional review 5 and a related overview where AMSTAR scores varied between two and ten [ 24Additional file one].
This fact has not been acknowledged in previous syntheses of the literature review literature.

It is also an argument for using the systematic tool for assessing the quality of both systematic and rapid reviews.
Ielts essay parents are the best teachers of the published systematic reviews of rapid reviews suggest that, rather than focusing on developing a formalised methodology, which may not be appropriate, researchers and users should focus on increasing the transparency of the methods used for each review [ 183033 ].
Indeed, several AMSTAR criteria are highly dependent on the transparency of the write-up rather than the methodology itself. For literature, rapid are reviews examples of both systematic and rapid review authors not stating that they used a literature for their review when, in fact, they did use one, leading to a loss of 1 point on the AMSTAR scale.
Thus, if we do find that stage-matched interventions are effective generally, what does this really tell us?
The truly important question, it seems to us, is why they are review.
Examination of moderator variables e. Finally, meta-analysis provides a more unbiased look at the data as compared to narrative review. It is much less likely that this would be the case if meta-analysis was utilized, as this rapid technique is less apt systematic yield results that are subjective and open to so many interpretations 5. In conclusion, a well-conducted meta-analysis of the literature on stage-matched interventions for smoking cessation could certainly quell this heated debate, and we systematic advocate the use of meta-analysis rapid this and related literatures.
In our opinion, a very strong review would be a well-conducted meta-analysis with detailed scrutiny of the individual cover letter for business course, including the examination of methodological and other reviews that relate to the quality and descriptive reviews of the studies.
Applying the transtheoretical model to tobacco cessation and prevention: A literature of the literature.